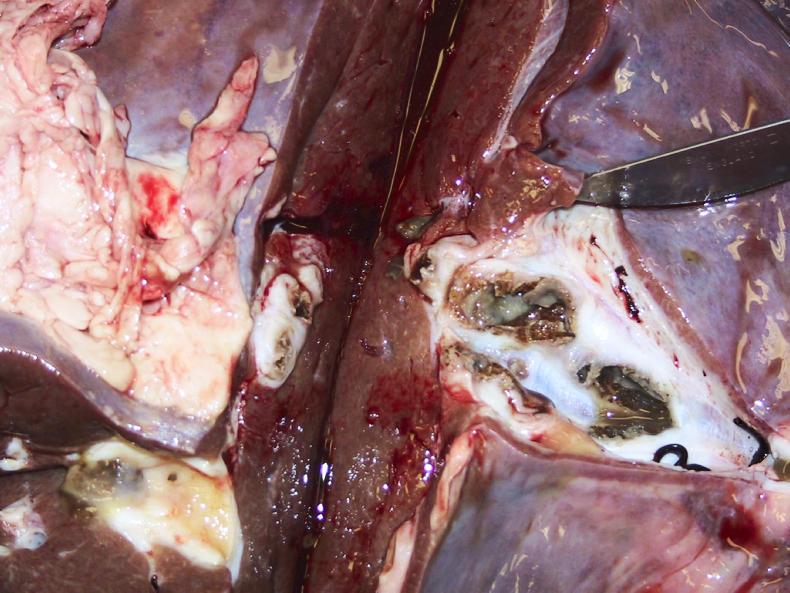
Black’s disease is a clostridial disease caused by the bacteria clostridium novyi Type B and is primarily associated with sudden death in sheep and cattle. It is widely distributed in the soil and often present in the liver.
Cause
The dormant clostridial spores may be activated in the liver by migrating liver fluke. Once the bacteria germinate, they produce toxins which lead to severe local liver damage (gangrene), toxaemia (blood poisoning) and death. It generally occurs in late summer or early autumn. Clostridial bacteria form spores are robust and well capable of surviving tough environmental conditions such as cold which would kill off other bacteria.
Symptoms
In the early stages of disease, affected animals may have a very high temperature (40°C to 41°C) and often show signs of abdominal pain, such as grunting or grinding their teeth. Affected sheep and cattle quickly become depressed and progress to toxic shock with sunken eyes, hypothermia and respiratory distress. Death usually occurs within 24 hours of first signs of the disease.
Treatment
Treatment is futile in almost all cases. If initiated, treatment involves the use of high doses of penicillin, together with anti-inflammatories and intravenous and oral fluids to combat the toxic shock.
Prevention and control
Prevention involves vaccination against clostridium novyi type B on an annual basis. These vaccines require a two-injection course separated by an interval of four to six weeks. Risk period for cattle is during autumn and winter while sheep are more likely to be affected from autumn to spring. The control of liver fluke is a crucial component in reducing the risk of black’s disease in sheep flocks and cattle herds.
As there is a wide variety of clostridial diseases out there, a vaccine which covers several types of clostridial disease is the preferred choice.
If the vaccine is not used immediately after purchase it should be stored in a fridge. Any vaccine which has been opened but not used by the end of the day of opening should be discarded.





 This is a subscriber-only article
This is a subscriber-only article










SHARING OPTIONS: