Suggested Solutions to student activities
1. Explain the term B.O.D. Biochemical Oxygen Demand.
Answer: B.O.D is the amount of dissolved oxygen consumed by a biological action when a sample of water is kept in the dark for 5 days at 20°C.
2. What are the implications of having a high B.O.D. in slurry?
Answer: High B.O.D means that the slurry has the potential to cause high levels of pollution once it reaches waterways. Fish may be killed and lots of aquatic life will also be killed off. There will be a rancid smell coming from the waterway.
Student activity: video clip answers
1.Identify two breeds of animals that are exiting the shed. List four bodily characteristics of these animal.
Answer: Limousin or Charolais –
1. Well fleshed,
2. Good conformation,
3. Block shaped,
4. Top and bottom line are parallel.
2. Name the four main gases that are releases during the agitation process
Answer: hydrogen sulphide, methane, ammonia [pungent smell], carbon dioxide.
3. Why are these gases so dangerous?
Answer: Inhaling thses cases can cause death. It’s difficult to smell these gases at high concentrations.
4. State two precautions that should be taken when carrying out the agitation process
Answer:
Conduct the process on a windy day.Stay clear of the sheds for the first 30 minutes at least.Have good ventilation in the sheds.Have all animals evacuated.Tell someone you are conducting the process. Signs need to be placed close to the shed.Keep all children and visitors away from the agitation process. 5. It is suggested that winter slurry has the highest concentration of gases. Why do you think that is?
Answer: The animals are in the shed for a number of months, fed silage and concentrates and so more noxious gases are produced by the micro- organisms in the tank. The slurry hasn’t been disturbed for months.
6.What are the ideal weather conditions to carry out the agitation process?
Answer: windy, breezy conditions.
7. What best practice measures did you observe on this farm around the agitation/slurry spreading process
Answer:
Fencing of 1.8m in height around open slurry pits.Temporary covers over the manhole covers. Safety signs erected where the process is taking place.Checks that all machines are in correct working order.Checks for overhead electricity lines when in the fields.Makes sure the mirrors on the tractor are clean and that the driver has full visibility.Farm animals: student activity
1.Can you suggest three reasons why a bull may be used on a farm?
Answer:
Good carcass quality sire.The bull detects oestrous.Produces good-quality, small calves, reducing problems with birthing process.2. From a farm safety point of view a farmer may use A.I. or some heat detection methods. State two advantages and two disadvantages of A.I.
Answer:
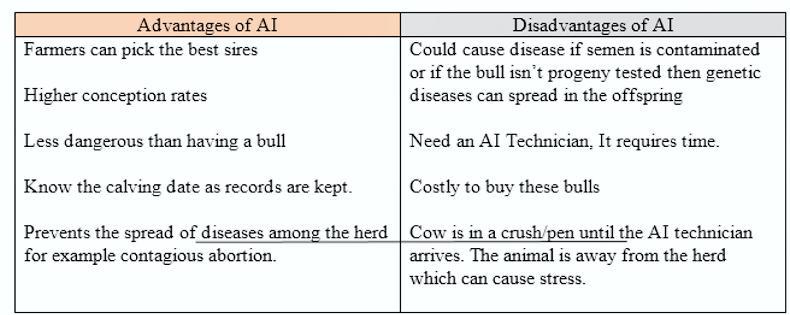
3. List three methods of heat detection that a dairy farmer may use on his/her farm.
Answer:
1. Chinball harness.
2. Tail painting.
3. Scratch cards.
Draw a diagram of a crush that is found on a dairy farm. Label on your diagram showing where the cattle exit and enter the crush.
Answer:
Ensure it is large.Labelled.Has an entrance and an exit.Head lock in place.A back gate.List four benefits of having a crush on a farm
Answer:
1. Dose the Animals
2. Tag the animals
3. TB testing
4. Inseminating the animals
5. Hoof pairing
6. Dehorning
7. Scanning the animals
8. Fostering – allowing calves to suckle the foster mother.
Crops safety: student activity
1. To which family does Ragwort and Buttercup belong to?
Answer:
Compositeae or Asteraceae = Ragwort Ranunculaceae = Buttercup2. Chemical control of weeds is control through the use of herbicides. Some herbicides are classified as total herbicides and some are classified as selective herbicides. Distinguish between these two terms that are in italics.
Answer:
Total herbicides are non-selective chemicals that kill a range of annual and perennial weeds in a pasture.Selective Herbicides are chemicals that kill certain weeds in a pasture but does not injure crop plants.3. Name three problems associated with the spraying of herbicides on crops.
Answer:
They can contaminate the soil and kill the soil microflora.They can seep into the rivers and water ways and kill the aquatic organisms.They can be toxic to insects and birds that feed on these crops.They can be toxic to human health if ingested or inhaled.Student activity: page 59
1. Name two types of compound fertilisers and name two types of straight fertilisers
Answer:
Compound= 10 : 10 : 20 or 18 : 6 : 12 or 27 : 2.5 : 5Straight = urea or CAN or ground rock phosphate.2. What are the implications of spreading excessive amounts of fertilisers on the land?
Answer:
Can be washed into the rivers and lakes and cause eutrophication.Can cause the crops to grow too fast and it can cause lodging.Can be a waste of money, depending on the time of year for example the autumn time there will be less growth of crops.If too much fertiliser is spread on a crop (eg potatoes) it can cause a watery tuber. 3. Before spreading a fertiliser a soil test needs to carried out on the farm. Describe how a soil test is carried out?
Answer:
Use a soil auger taking 20 to 25 samples in a random W shaped pattern over the land. Do not take samples from water logged areas, poached areas, near gates, under trees as they may give in accurate and unreliable result.4. Some plants have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates in the soil. State the name of one plant that can carry out this process and name the process involved.
Answer:
Clover that belongs to the family Leguminoseae or Fabaceae.Nitrogen fixation.If you have any questions in relation to the content covered in the agricultural science study guides, feel free to email your questions to agsci@farmersjournal.ie
Suggested Solutions to student activities
1. Explain the term B.O.D. Biochemical Oxygen Demand.
Answer: B.O.D is the amount of dissolved oxygen consumed by a biological action when a sample of water is kept in the dark for 5 days at 20°C.
2. What are the implications of having a high B.O.D. in slurry?
Answer: High B.O.D means that the slurry has the potential to cause high levels of pollution once it reaches waterways. Fish may be killed and lots of aquatic life will also be killed off. There will be a rancid smell coming from the waterway.
Student activity: video clip answers
1.Identify two breeds of animals that are exiting the shed. List four bodily characteristics of these animal.
Answer: Limousin or Charolais –
1. Well fleshed,
2. Good conformation,
3. Block shaped,
4. Top and bottom line are parallel.
2. Name the four main gases that are releases during the agitation process
Answer: hydrogen sulphide, methane, ammonia [pungent smell], carbon dioxide.
3. Why are these gases so dangerous?
Answer: Inhaling thses cases can cause death. It’s difficult to smell these gases at high concentrations.
4. State two precautions that should be taken when carrying out the agitation process
Answer:
Conduct the process on a windy day.Stay clear of the sheds for the first 30 minutes at least.Have good ventilation in the sheds.Have all animals evacuated.Tell someone you are conducting the process. Signs need to be placed close to the shed.Keep all children and visitors away from the agitation process. 5. It is suggested that winter slurry has the highest concentration of gases. Why do you think that is?
Answer: The animals are in the shed for a number of months, fed silage and concentrates and so more noxious gases are produced by the micro- organisms in the tank. The slurry hasn’t been disturbed for months.
6.What are the ideal weather conditions to carry out the agitation process?
Answer: windy, breezy conditions.
7. What best practice measures did you observe on this farm around the agitation/slurry spreading process
Answer:
Fencing of 1.8m in height around open slurry pits.Temporary covers over the manhole covers. Safety signs erected where the process is taking place.Checks that all machines are in correct working order.Checks for overhead electricity lines when in the fields.Makes sure the mirrors on the tractor are clean and that the driver has full visibility.Farm animals: student activity
1.Can you suggest three reasons why a bull may be used on a farm?
Answer:
Good carcass quality sire.The bull detects oestrous.Produces good-quality, small calves, reducing problems with birthing process.2. From a farm safety point of view a farmer may use A.I. or some heat detection methods. State two advantages and two disadvantages of A.I.
Answer:

3. List three methods of heat detection that a dairy farmer may use on his/her farm.
Answer:
1. Chinball harness.
2. Tail painting.
3. Scratch cards.
Draw a diagram of a crush that is found on a dairy farm. Label on your diagram showing where the cattle exit and enter the crush.
Answer:
Ensure it is large.Labelled.Has an entrance and an exit.Head lock in place.A back gate.List four benefits of having a crush on a farm
Answer:
1. Dose the Animals
2. Tag the animals
3. TB testing
4. Inseminating the animals
5. Hoof pairing
6. Dehorning
7. Scanning the animals
8. Fostering – allowing calves to suckle the foster mother.
Crops safety: student activity
1. To which family does Ragwort and Buttercup belong to?
Answer:
Compositeae or Asteraceae = Ragwort Ranunculaceae = Buttercup2. Chemical control of weeds is control through the use of herbicides. Some herbicides are classified as total herbicides and some are classified as selective herbicides. Distinguish between these two terms that are in italics.
Answer:
Total herbicides are non-selective chemicals that kill a range of annual and perennial weeds in a pasture.Selective Herbicides are chemicals that kill certain weeds in a pasture but does not injure crop plants.3. Name three problems associated with the spraying of herbicides on crops.
Answer:
They can contaminate the soil and kill the soil microflora.They can seep into the rivers and water ways and kill the aquatic organisms.They can be toxic to insects and birds that feed on these crops.They can be toxic to human health if ingested or inhaled.Student activity: page 59
1. Name two types of compound fertilisers and name two types of straight fertilisers
Answer:
Compound= 10 : 10 : 20 or 18 : 6 : 12 or 27 : 2.5 : 5Straight = urea or CAN or ground rock phosphate.2. What are the implications of spreading excessive amounts of fertilisers on the land?
Answer:
Can be washed into the rivers and lakes and cause eutrophication.Can cause the crops to grow too fast and it can cause lodging.Can be a waste of money, depending on the time of year for example the autumn time there will be less growth of crops.If too much fertiliser is spread on a crop (eg potatoes) it can cause a watery tuber. 3. Before spreading a fertiliser a soil test needs to carried out on the farm. Describe how a soil test is carried out?
Answer:
Use a soil auger taking 20 to 25 samples in a random W shaped pattern over the land. Do not take samples from water logged areas, poached areas, near gates, under trees as they may give in accurate and unreliable result.4. Some plants have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates in the soil. State the name of one plant that can carry out this process and name the process involved.
Answer:
Clover that belongs to the family Leguminoseae or Fabaceae.Nitrogen fixation.If you have any questions in relation to the content covered in the agricultural science study guides, feel free to email your questions to agsci@farmersjournal.ie







 This is a subscriber-only article
This is a subscriber-only article






